Apple Inc. developed the HLS protocol to improve audio and video content delivery over the Internet. The first version of the protocol was introduced in 2010, and since then, it has been through several iterations, with each new version bringing improvements and added features. The latest version of the protocol, HLS v4, was released in 2016.
In this article, let's better understand Low Latency HLS and the latencies important for good video streaming. Let's start with the basics first.
What is low latency?
"Low latency" refers to a short delay between when an action is initiated and when it is carried out. In the context of computer networking, it is often used to describe the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. Low-latency networks are important for applications that require quick response times, such as Live Streaming. With the increase in video streaming, low-latency streaming is also being widely used.
What is low latency HLS?
Low latency HLS is an HTTP-based streaming protocol designed to reduce the delay between a user requesting a stream and the start of playback - to reduce video latency. Low latency HLS works by reducing the time it takes to send data from the origin server to the player. This is done by sending small chunks of data, called segments, rather than large files. The segments are then reassembled at the player so that they can be played back in real-time.
Low latency HLS has been shown to reduce delays by up to 50% compared to regular HLS streams. This can be a major benefit for live streaming applications, such as sports or news events, where every second counts. Low latency HLS is also useful for on-demand streams where viewers are impatient and may abandon a stream if it takes too long to start.
To use low latency HLS, you need to create a special playlist file that tells the player how to request the segments. The playlist file must be served over HTTP, so it can be used with any web server. You also need to make sure that your origin server is configured to send the segments in the proper format. Finally, you need to use a player that supports low latency HLS.
At this time, there are very few players that support low latency HLS. The most popular one is perhaps Apple's HTTP Live Streaming Tools, which are part of their XCode development environment. There are also a few open-source players, such as hls.js and videojs-contrib-hls.
How does Low latency HLS (LL HLS) work?
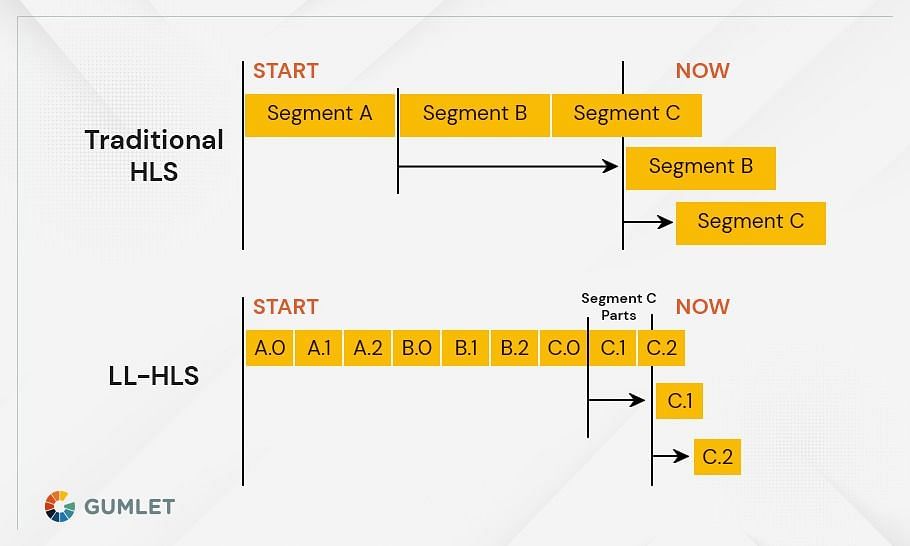
Low latency HLS (LL HLS) is a variation of the standard HLS protocol that reduces the delay between when a video is encoded and when it is played back. This reduction in delay, or latency, enables live streaming applications such as game streaming, financial news broadcasting, and live event coverage to provide a more immersive experience for viewers.
To achieve low latency, LL HLS introduces some changes to the way that video is encoded and packets are delivered:
- Videos are encoded using lower bitrates and shorter GOP sizes. This results in smaller packets that can be processed more quickly.
- LL HLS uses a new packet format that allows packets to be delivered out of order. This means that packets can be delivered as soon as they are encoded, rather than waiting for a complete GOP to be assembled.
- LL HLS uses an adaptive bitrate (ABR) algorithm that constantly monitors network conditions and makes real-time adjustments to ensure that packets are delivered as quickly as possible without being dropped.
When used together, these three changes result in a significant reduction in latency. In fact, LL HLS can reduce latency by up to 80% compared to standard HLS, making it an ideal solution for live streaming applications that require low latency.
Is low latency better for streaming?
There are a few things to keep in mind when thinking about whether or not low latency is better for streaming. First, it's important to understand what latency is and how it can affect streaming. Generally, latency is the time it takes for a signal to travel from one point to another. In streaming, latency is the time it takes for a video or audio signal to travel from the source (the person or camera broadcasting the stream) to the destination (the person watching or listening to the stream).
Latency can have a major impact on the quality of a stream. If there is much latency, it can cause issues like lip-syncing problems, choppy video, and dropped frames. On the other hand, if there is too low video latency, it can cause problems like buffering and delays. Hence, it is important to track latency metrics.
Low latency for both HLS and MPEG-DASH is around 2-5 seconds. This gives viewers a good experience without causing too many issues for the broadcaster.
Ultimately, it's up to the broadcaster to decide what latency works best for them and their audience. If you're not sure what to choose, it's always a good idea to start with higher latency and then lower it if you find that viewers are having issues with the quality of your stream - eventually, you can reach the low latency streaming level.
How can I reduce my latency HLS?
There are a few ways that you can reduce your latency when using HLS. One way is to use a lower bitrate for your stream. This will reduce the amount of time it takes for each frame to be encoded and sent out. Another way is to use a smaller buffer size. This will also help reduce the latency since it takes less time to fill up the buffer and send out the data. Finally, you can try using a different codec all together. For example, if you're using HLS with h264, you could try switching to h265. This codec is newer and has better compression, which can lead to lower latency overall. Learn more about H.264 vs. H.265. Whichever method you choose, make sure to test it out beforehand to see what works best for you.
Low latency is crucial for many applications where real-time interaction is required, such as live sports or gaming. It also makes HLS well-suited for use cases where the network conditions are variable or unpredictable, such as mobile networks.
What is a Good Low Latency Streaming?
In short, a good latency for streaming is around 2-5 Seconds. This gives the viewer a chance to see the action as it happens without feeling like they're watching a recording. So if you're looking to get the best streaming experience for your viewers, aim for a latency of 2-5 seconds.
Conclusion
One of the main selling points of HLS is its low latency compared to other streaming protocols. This is achieved by splitting the stream into small segments, which are then served sequentially to the client. This allows the client to start playback almost immediately without having to wait for the entire stream to be downloaded first.
Overall, HLS is a very versatile and widely-used streaming protocol thanks to its low latency and compatibility with a variety of devices and platforms. It is an ideal choice for applications where real-time interaction is required or where network conditions may be variable.
At Gumlet, we support the HLS + DASH video formats. Check out the documentation for detailed instructions!
FAQs
1. Is low latency better for streaming?
Yes, low latency is better for streaming, as it reduces the time it takes for content to be transmitted from the source to the user, allowing for a smoother streaming experience.
2. What is the use of HLS?
HLS makes media content delivery more reliable and efficient by using adaptive bitrate streaming technology, which helps ensure that viewers get the best video and audio quality.
3. Which is better, HLS vs. RTMP?
HLS is the better option for streaming media because it is more reliable, more secure, and supports a wider range of devices. RTMP, on the other hand, is less reliable and less secure but provides better latency, meaning faster streaming and smoother playback.
4. Is HLS free?
Yes, HLS is free to use.