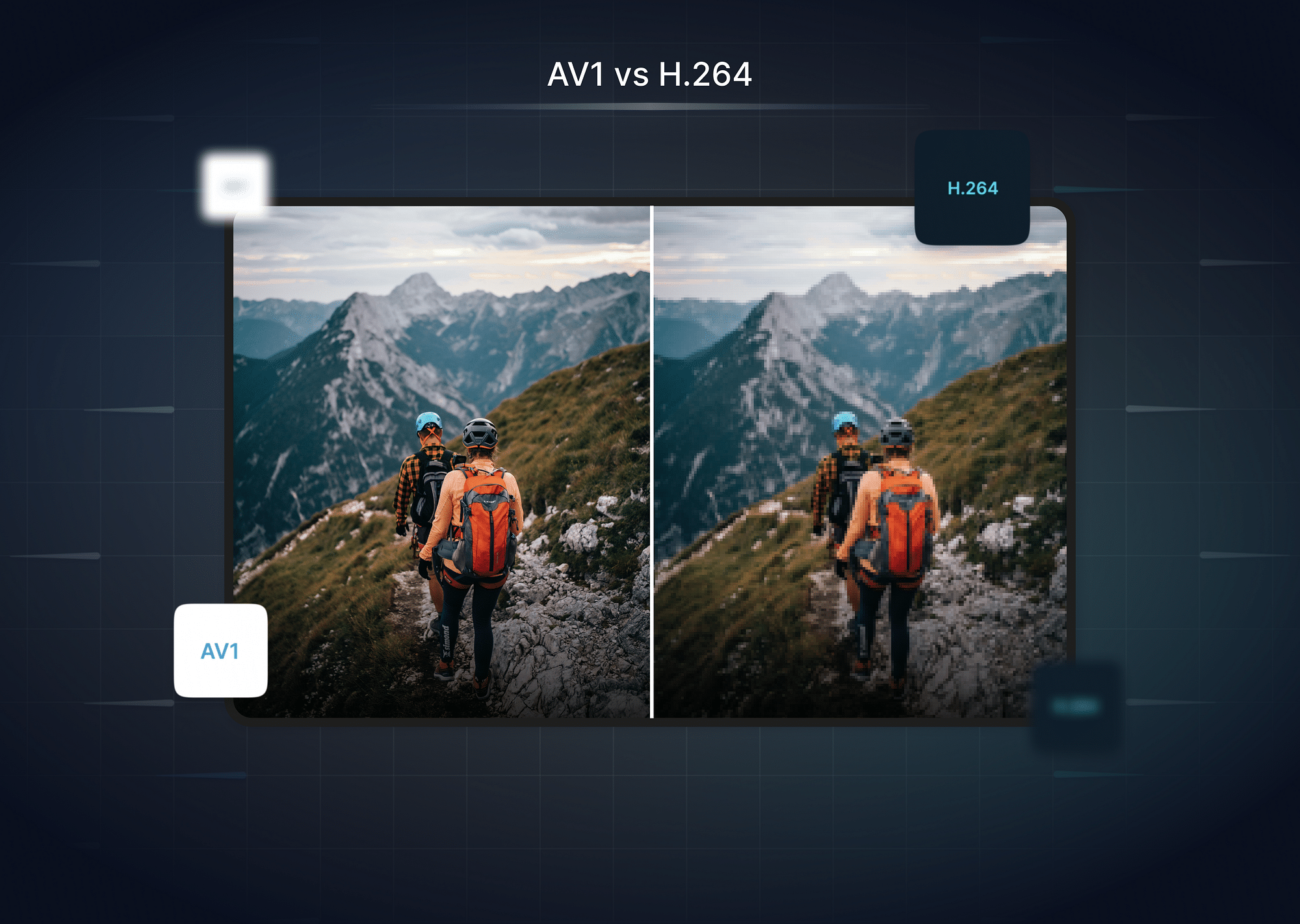
When it comes to video compression, H.264 and AV1 are two of the most discussed codecs in the industry. While H.264 (AVC) has been the dominant standard for over a decade, AV1 is a newer, more advanced codec that promises better compression efficiency. But which one is truly better? Let’s break it down.
What is H.264?
H.264, officially known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), was developed in 2003 as a joint project between the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group and the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group. Its widespread adoption across streaming platforms, digital broadcasting, and Blu-ray has made it the backbone of modern video compression.
Some of the key features of the H.264 include:
- High Compression Efficiency: H.264 balances file size reduction with video quality, making it ideal for streaming.
- Broad Compatibility: Supported by most hardware and software platforms worldwide.
- Real-Time Encoding and Decoding: Suited for live streaming and video conferencing.
Pros and Cons of H.264
Here are some of the important pros and cons associated with the use of H.264.
Pros:
- Works Everywhere: H264 is like the universal language of video codecs—nearly every device and app speaks it fluently.
- Rock-Solid Stability: With decades of fine-tuning, H.264 is dependable and gets the job done seamlessly.
Cons:
- It’s Not Free: If you’re using H264 for commercial purposes, those pesky licensing fees can add up.
- Not the Most Efficient: When compared to newer codecs like AV1 and H.265, H.264 falls short in terms of compression efficiency.
What is AV1?
Developed by the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia), AV1 was introduced in 2018 to address the increasing demand for efficient and royalty-free video compression. It is designed to surpass older codecs like H.264 and VP9 in compression efficiency while maintaining high video quality.
Here are some features to look out for when it comes to AV1:
- Royalty-Free Licensing: Eliminates the costs associated with proprietary codecs.
- Advanced Compression: Achieves better quality at lower bit rates compared to H264.
- Future-Ready Technology: Optimized for 4K, 8K, and next-gen content.
Pros and Cons of AV1
Here are some pros and cons of AV1:
Pros:
- Top-Notch Compression: AV1 shrinks file sizes dramatically while keeping your video looking amazing.
- Free for Everyone: It’s open-source and royalty-free, which means no extra costs for developers or businesses.
Cons:
- Takes Its Time: Encoding with AV1 can feel like waiting in a long line—it’s slower than H264.
- Not Everywhere Yet: AV1 playback might be a challenge on older devices without hardware support.
Difference Between AV1 and H.264
Looking for differences between AV1 and H.264? This table below summarises all the important differences succinctly:
| Feature | H.264 | AV1 |
|---|---|---|
| File Size | Larger compared to AV1 | Smaller due to better compression |
| Video Quality | High but less efficient at low bitrates | Better quality at lower bitrates |
| Compression Efficiency | Moderate | Excellent |
| Encoding Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Decoding Speed | Faster | Slower without hardware support |
| Hardware Support | Widely supported | Limited to newer devices |
| Quality at Low Bitrates | Moderate | Excellent |
| Licensing | Proprietary | Royalty-Free |
| Applications | Streaming, broadcasting, live video | Streaming, 4K/8K content, next-gen media |
Let’s look at these parameters and how the two differ in a bit more detail:
- File Size: H.264 requires more storage space for videos, as its compression is less efficient. On the other hand, AV1 excels in shrinking file sizes without sacrificing quality. This makes AV1 a better choice for those dealing with storage constraints or streaming high-resolution videos over limited bandwidth.
- Video Quality: While H.264 provides decent quality, it struggles at lower bitrates, leading to noticeable artifacts. AV1, however, maintains superior quality even at reduced bitrates, making it ideal for streaming platforms aiming for high-quality playback under varying network conditions.
- Compression Efficiency: H.264 offers moderate compression, which was groundbreaking at the time of its release. AV1, with its advanced algorithms, achieves far better compression, allowing for smaller files with the same or better visual fidelity. This makes AV1 a futuristic choice for efficient video distribution.
- Encoding Speed: H.264 is faster at encoding, which is a significant advantage for real-time applications like live streaming. AV1, while slower, focuses on efficiency, making it better suited for content that isn’t time-sensitive, such as pre-recorded videos.
- Decoding Speed: Videos encoded in H.264 are easier to decode, thanks to universal hardware support. AV1’s decoding can lag on older devices unless they have the necessary hardware acceleration, which limits its usability on legacy systems.
- Hardware Support: H.264 has had years to establish itself and is compatible with almost every device and platform. AV1, being newer, is limited to modern devices with specific hardware support, although this is gradually improving.
- Quality at Low Bitrates: At lower bitrates, H.264 shows its age with quality degradation. AV1 shines in this area, delivering crisp visuals even when bandwidth is tight, making it an excellent choice for streaming in less-than-ideal network conditions.
- Licensing: H.264 comes with licensing fees, which can increase costs for commercial applications. AV1, in contrast, is entirely royalty-free, making it an attractive choice for businesses seeking cost-effective solutions.
- Applications: H.264 remains a staple for traditional use cases like live video and broadcasting. AV1, however, is better suited for cutting-edge applications such as 4K/8K streaming and next-generation media content, positioning it as the codec of the future.
While both codecs serve different needs, AV1’s compression efficiency and royalty-free nature make it a more forward-looking choice for high-quality content in 2026.
H.264 vs AV1: Which is Better? An Expert Opinion
If you need compatibility, low-latency streaming, and quick encoding, H.264 is still the best option today. However, if you prioritize efficiency, cost savings, and future scalability, AV1 is the better choice—especially for platforms focusing on high-quality, bandwidth-efficient streaming. Furthermore, its royalty-free model is a cost-effective solution for businesses.
For now, H.264 remains the industry standard, but as hardware and software adoption improve, AV1 is positioned to take over in the coming years. The shift won’t happen overnight, but as more devices support AV1 decoding, it will likely become the go-to codec for modern streaming.
👉 Verdict: If you need immediate reliability, stick with H.264. If you’re preparing for the future, start integrating AV1 now. For content creators, streaming services, or businesses prioritizing long-term cost-effectiveness and cutting-edge compression technology, AV1 is the way to go.
How to Convert H.264 to AV1 and Vice Versa?
Converting between H.264 and AV1 is straightforward with FFmpeg, a versatile multimedia tool widely used for video processing tasks. Whether you're looking to reduce file size, enhance video quality, or adapt to modern codecs, FFmpeg has you covered. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
1. Install FFmpeg: First, download and install FFmpeg on your system. You can find the installation guide for your operating system here. Once installed, ensure it’s added to your system’s PATH for easy access via the command line.
2. Convert H.264 to AV1: To convert a video from H.264 to AV1, use the following command:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -c:v libaom-av1 output_av1.mp4Replace input.mp4 with your source file name and output_av1.mp4 with the desired output file name. This command utilizes the AV1 codec (libaom-av1) to encode the video.
3. Convert AV1 to H.264: To switch from AV1 to H.264, use this command:
ffmpeg -i input_av1.mp4 -c:v libx264 output_h264.mp4Here, libx264 specifies the use of the H.264 codec for encoding. Adjust input_av1.mp4 and output_h264.mp4 to match your file names.
4. Adjust Encoding Settings: FFmpeg allows for fine-tuning the encoding process with additional flags. For example:
To set a specific bitrate:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -c:v libaom-av1 -b:v 2M output_av1.mp4To control quality:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -c:v libaom-av1 -crf 30 output_av1.mp4Experiment with parameters like -b:v (bitrate) and -crf (constant rate factor) to achieve your desired quality and file size balance.
These commands make it easy to transition between H.264 and AV1, enabling you to take advantage of AV1’s advanced compression or H.264’s broader compatibility, depending on your needs.
To Summarize
- If you need a codec that offers superior compression efficiency, reduced file sizes, and better quality at lower bitrates, AV1 is the obvious choice. Its royalty-free nature also makes it an economical option for businesses looking to cut licensing costs.
- However, the slower encoding speed and limited hardware support of AV1 might present challenges, particularly for real-time applications or users relying on older devices.
- As AV1 continues to gain traction, it’s poised to become the go-to codec for streaming platforms, next-gen content like 4K and 8K, and any scenario where bandwidth efficiency is critical.
- On the other hand, H.264 remains a reliable and practical choice for many scenarios, especially where compatibility and speed are key concerns. Its universal support across devices and platforms ensures seamless playback and integration, making it ideal for legacy systems or live-streaming events where speed and stability are paramount.
- While AV1 represents the future of video compression, H.264’s proven track record and extensive optimization mean it’s far from obsolete.
FAQs
1. Is H.264 good for 4K?
Yes, H.264 supports 4K video and delivers high-quality visuals. However, it requires higher bitrates to maintain quality compared to newer codecs like AV1. While this may not be an issue for many, it can lead to larger file sizes and increased bandwidth requirements during streaming.
2. Does AV1 use less bandwidth?
Absolutely. AV1’s advanced compression technology ensures that it uses significantly less bandwidth while maintaining the same level of video quality. This makes it an excellent choice for streaming high-resolution content, especially in situations where network speeds are limited.
3. Is AV1 encoding slower than H.264?
Yes, encoding with AV1 is slower because of its highly sophisticated algorithms designed for superior compression and quality. While this slower speed may not matter for pre-recorded content, it could be a limitation for real-time encoding scenarios.
4. Is H.264 good for YouTube?
Yes, H.264 remains one of the most widely supported codecs on YouTube. Its compatibility across virtually all devices and platforms makes it a preferred choice for video uploads, ensuring smooth playback for viewers worldwide.
5. Is AV1 suitable for live streaming?
AV1 can be used for live streaming, but its real-time encoding requires advanced hardware support. Without dedicated AV1 hardware encoders, the processing speed may not be fast enough for live broadcasts, making it better suited for pre-encoded content.