Bitrate is the rate at which data is transmitted in a specific time frame, typically measured in bits per second (bps). The bitrate of a video significantly impacts its perceived quality. A higher bitrate generally results in better video quality but also means larger file sizes and higher bandwidth requirements. There are two primary methods for managing bitrate in video encodingto: Constant Bitrate (CBR) and Variable Bitrate (VBR). CBR maintains a consistent bitrate throughout the entire video, while VBR adjusts the bitrate based on the complexity of each scene.
What is CBR?
Constant Bitrate (CBR) keeps the data rate constant for the duration of the video. This indicates that, regardless of the complexity of the content, the video is encoded at a fixed bitrate. The bitrate stays the same whether the scene is still or is moving quickly.
Pros of CBR:
- Consistent quality: A predictable watching experience is offered by the video's comparatively constant quality, which is the result of the bitrate being fixed.
- Simple to manage: It's easier to plan for storage and bandwidth needs because the bitrate is consistent.
Cons of CBR:
- Ineffective use of bandwidth: Because CBR gives both basic and complicated scenes the same amount of data, it might be inefficient. File sizes grow as a result of this.
- Potential quality issues in complex scenes: To maintain a constant bitrate, complex scenes might suffer from quality degradation, such as blockiness or artifacts.
What is VBR?
The data rate is modified by Variable Bitrate (VBR) according to the complexity of the video content. In contrast to CBR, VBR allots more bits to more complex scenes (like action sequences and intricate visuals) and fewer bits to situations that are simpler (like low motion and static images). The goal of this dynamic bit allocation is to maximize video quality while maintaining a manageable file size.
Pros of VBR:
- Effective use of bandwidth: VBR reduces file sizes by using fewer bits in less complicated scenes.
- Better overall video quality: The ability to adapt to content complexity often leads to a higher overall perceived video quality.
Cons of VBR:
- Possible buffering problems: Buffering is more likely to occur when bitrate varies, particularly on unstable networks.
- More difficult to handle: Because of the fluctuating bitrate of VBR, it is more difficult to estimate file sizes and bandwidth needs.
Difference Between CBR and VBR
| Aspect | Constant Bit Rate (CBR) | Variable Bit Rate (VBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Consistent quality throughout, but may suffer in complex scenes. | Higher quality in complex scenes, lower in simpler scenes. |
| File Size | Predictable and fixed file sizes. | Unpredictable and variable file sizes. |
| Bandwidth Usage | Steady and predictable bandwidth usage. | Efficient bandwidth usage, but variable. |
| Ideal Scenarios | Live streaming, broadcasting, and situations where a predictable file size is crucial. | Pre-recorded content, high-quality media, and efficient storage usage. |
| Application Examples | Live sports, news broadcasts, and online streaming platforms | Movies, music, and downloadable content. |
| Settings Complexity | Generally simpler to set up and configure. | Requires more fine-tuning and understanding of content complexity. |
Quality
Although CBR keeps the media file's quality constant throughout, it might not give complicated scenes adequate bitrate, which could result in decreased quality. On the other hand, VBR adjusts the bitrate according to the intricacy of the video, giving complicated scenes a higher bitrate allocation and simpler scenes a lower bitrate. Higher overall quality is the outcome, especially in scenes with a lot of motion or detail. Simpler sequences get a lower bitrate, so the quality can differ throughout the file.
Bandwidth Usage
When using CBR, the bandwidth usage is steady and predictable, making it ideal for live streaming and broadcasting where consistent delivery is crucial. CBR ensures that the bit rate remains fixed, which can lead to inefficient use of bandwidth during simpler scenes. In contrast, VBR adjusts the bit rate based on the complexity of the content, leading to more efficient bandwidth usage. This variability, however, can result in fluctuating bandwidth demands, which might pose challenges for real-time streaming and require more robust network management.
Settings Complexity
When it comes to settings complexity, CBR is generally simpler to set up and configure because it maintains a constant bit rate throughout the media file, requiring minimal adjustment. On the other hand, VBR requires more fine-tuning and a deeper understanding of the content's complexity to optimize the bit rate dynamically, making the setup process more intricate. VBR settings often involve specifying a range for the bit rate and additional parameters to balance quality and file size effectively.
What is Rate Control?
Rate control is an important part of video encoding since it determines how much data (bitrate) is used for each frame or segment of the video. It guarantees the encoded video stays inside a certain bitrate target. Rate control is essential for balancing video quality and file size.
Different Types of Rate Control Modes
Basic:
- Constant Bitrate (CBR): Maintains a fixed bitrate throughout the video, regardless of content complexity.
- Variable Bitrate (VBR): Adjusts the bitrate based on the complexity of each scene, allocating more bits to complex scenes and fewer to simpler ones.
Advanced:
- Average Bitrate (ABR): Sets a target average bitrate but allows fluctuations within a defined range.
- Constant Quantization Parameter (CQP): Controls video quality by setting a constant quantization parameter, indirectly affecting the bitrate.
- 2-Pass Encoding: Analyzes the video content in a first pass to estimate optimal bitrate allocation, followed by encoding in a second pass based on the analysis.
When to Use CBR and VBR
The choice between CBR and VBR largely depends on the specific requirements of your video project.
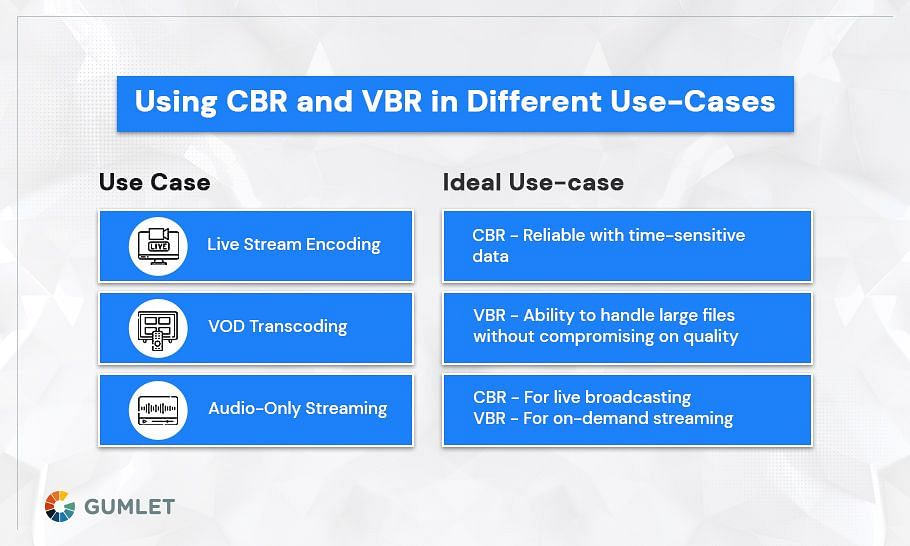
When to Use CBR:
- Live Streaming: CBR guarantees constant video quality despite changing network conditions, ensuring a seamless watching experience and avoiding buffering issues.
- Real-Time Applications: CBR's consistent performance is beneficial for online gaming, video conferencing, and other real-time applications.
- Low Bandwidth Environments: CBR helps prevent buffering by maintaining a steady data rate in scenarios with limited bandwidth.
When to Use VBR:
- On-Demand Videos: VBR is ideal for pre-recorded content like movies, TV shows, and music videos, adjusting bit rate based on scene complexity to provide higher quality and save space.
- Adaptive Streaming: VBR excels in adaptive streaming, encoding content at multiple bit rates to adapt to varying network conditions for a seamless viewing experience.
- Downloadable Content: VBR optimizes file size without compromising quality, making it suitable for high-quality downloadable content.
Conclusion
Rate control modes are extremely important if you have to get the most out of your media files. You should select a rate control mode based on your requirements. Both CBR and VBR play distinct roles and it is important for you to know which of the two options suits your case the best. The bottom line is that CBR is best for time-sensitive situations whereas VBR is for on-demand video.
FAQs
- Is VBR 2 pass better than VBR 1 pass?
Yes, VBR 2 pass is generally better than VBR 1 pass because it analyzes the content during the first pass to optimize bit rate distribution in the second pass, resulting in higher quality and more efficient encoding.
- Which software is used for CBR and VBR Encoding?
Popular software for CBR and VBR encoding includes Adobe Premiere Pro, HandBrake, FFmpeg, and Audacity (for audio).
- Should I use VBR or CBR for AAC?
For AAC (Advanced Audio Codec), VBR is usually preferred as it provides better overall audio quality and more efficient file sizes compared to CBR.
- Is CBR better than VBR 2 pass?
No, VBR 2 pass typically provides higher quality and more efficient encoding than CBR because it optimizes bit rate distribution based on content complexity.
- Which is better ABR vs CBR?
ABR (Average Bitrate) is often better than CBR as it offers a balance between quality and file size by maintaining an average bit rate, allowing for some variability to improve overall quality.