Music and audio are now essential elements of entertainment. Whether it's preserving cherished family videos or experiencing a fantastic theater show, the quality of sound plays a significant role in how enjoyable the experience is for listeners. Two well-known sound formats, FLAC and WAV, have been circulating online for years, and experts and enthusiasts continue to debate which is superior in terms of overall performance. Finally, we may have an answer to this long-standing question.
What is FLAC?
FLAC, or Free Lossless Audio Codec, is a popular digital audio format where files are compressed without losing data or quality. FLAC files are generally encoded at a bit depth of 16 or 24 bits and a sampling rate of up to 192 kHz, which makes them ideal for high-quality audio playback. In addition to this, FLAC files are compatible with relevant metadata that can be displayed by audio players, making it easier to manage and organize any audio collection.
Schedule a Demo with Our Video Expert!
Discover how Gumlet can help you build a cutting-edge video streaming infrastructure.
Pros of Using FLAC:
- It compresses audio files without compromising quality.
- FLAC files are highly compatible and can be played by various devices and audio players.
Cons of Using FLAC:
- They are not very suitable for streaming.
- They require higher CPU usage for decoding and encoding processes.
What is WAV?
WAV stands for Waveform Audio File Format. It is another widely used uncompressed digital sound format developed by Microsoft in collaboration with IBM. Because a WAV file produces high-quality outputs, it is popularly used in various professional audio applications. Unlike older, compressed audio formats like MP3 and AAC, WAV does not lose any data or quality while encoding the sound. As such, the file sizes are relatively larger. With a typical bit depth of 16 bits (maximum 32 bits) and a sampling rate of up to 192 kHz, WAV files are efficient at producing high-quality outputs.
Pros of Using WAV:
- It is an uncompressed format with no potential loss in quality.
- Very suitable for professional applications.
Cons of Using WAV:
- File sizes are comparatively larger than compressed audio file formats.
- There is limited support for high-resolution audio.
Difference Between FLAC and WAV
Getting a deeper understanding of both audio formats requires a detailed head-to-head comparison.
Here are the key differentiating factors that can settle the FLAC vs. WAV debate:
| Basis of Comparison | WAV | FLAC |
|---|---|---|
| File Size | The file size is generally larger. | FLAC files are typically smaller in comparison. |
| Compression | It is an uncompressed digital audio format. | It provides lossless compression; files are compressed without affecting the audio quality. |
| Quality | It produces high-quality sound. | It produces high-quality sound. |
| Compatibility | It is widely supported by all devices and software as it is an older format. | It is widely supported by newer platforms. But incompatible with many old audio players. |
| Sampling Rate | Up to 192 kHz | Up to 192 kHz |
| Bit Depth | It supports bit depths of 8, 16, 24, and 32 bits. | It supports bit depths of 8, 16, and 24 bits. |
| Bit Rate | The bit rate varies depending on the bit depth and sample rate used for a specific file. | It supports variable bit rates that typically range between 800 kbps and 1,400 kbps. |
| Editing Flexibility | Easily editable | Can be edited (but requires decompression) |
| Metadata Support | Limited (metadata support varies) | Yes (supports embedding album art, tags) |
| Streaming Compatibility | Less common for streaming due to larger file size | Commonly used for streaming services due to smaller file size |
| Licensing | Proprietary | Free and open source. |
File Size
FLAC files are undoubtedly smaller and require less storage because it is a compressed file format. WAV, on the other hand, is uncompressed. This implies that a WAV file contains all the original data without any changes. To give you an idea, a typical three-minute WAV file at 44.1 kHz and 16-bit depth would be around 32 MB in size. In FLAC format, the same file can be compressed to 12 MB.
Compression
FLAC files use lossless compression. This means that audio files are compressed but don't lose any quality or data. WAV files, on the other hand, are completely uncompressed.
Quality
There is not much to separate between WAV and FLAC in terms of quality, as both file formats can provide high-quality and high-fidelity sounds.
Compatibility
WAV is supported by all major platforms, including the old ones. FLAC also enjoys good compatibility options. However, because it is newer, it might not be supported by traditional players and software.
Sampling Rate and Bit Depth
The higher the sampling rate and bit depth, the better the overall performance, as it gives a better and more representation of the original audio signal. Both WAV and FLAC can support sampling rates of up to 192 kHz. WAV supports bit depths up to 32 bits. FLAC, on the other hand, only supports up to 24 bits.
Bit Rate
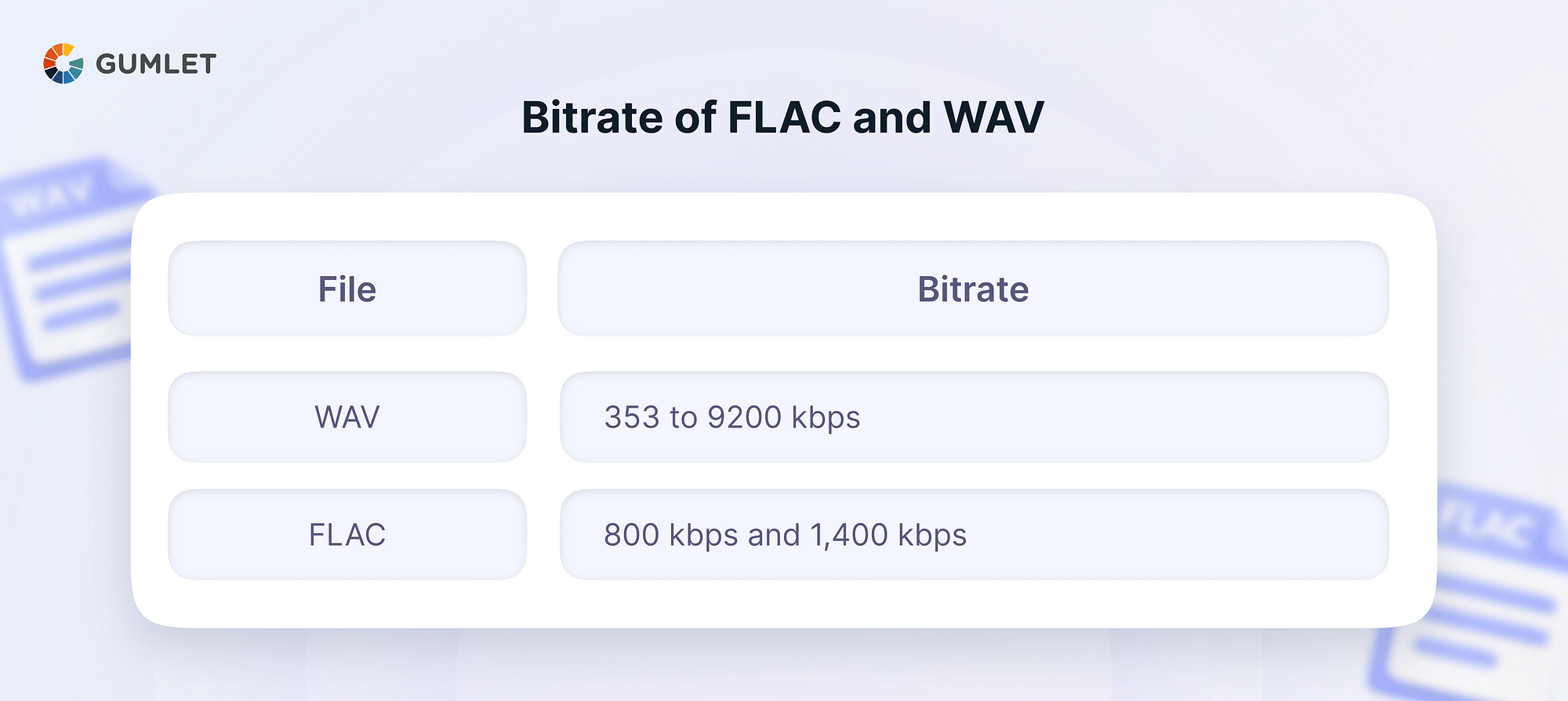
The higher the bit rates, the better the sound quality. However, higher bit rates also result in larger file sizes. The bit rates supported by either audio format depend on the sampling rates and bit depths. For a typical WAV file, the bit rate can be between 353 kbps for an 8-bit mono file at a sampling rate of 8 kHz to 9.2 MBPS for a 32-bit stereo file with a sampling rate of 192 kHz. On the other hand, FLAC files typically have bit rates between 800 kbps and 1,400 kbps.
Licensing
WAV is a proprietary audio format. It is not open-source. However, no licensing is required for its usage. FLAC, on the other hand, is completely free and open-source.
FLAC vs WAV: Which is Better?
For streaming, both FLAC and WAV have their own benefits and drawbacks. For example, WAV files offer a high-quality listening experience. But they are also bigger in size as the format is uncompressed. Thus, streaming WAV files will require more bandwidth and can be slower. FLAC files, on the other hand, are compressed and smaller in size. While they don't require as much bandwidth, they do demand more processing power to complete the decompressing process.
Overall, FLAC is considered the more suitable format because it enables faster streaming and produces higher-quality sound. However, the ultimate choice also depends on several other factors, such as users' specific requirements, the condition of their devices, and the platforms they use for streaming.
Use Cases of FLAC and WAV
Despite the many similarities between FLAC and WAV audio file formats, especially in terms of quality, they have many diverse use cases.
Let's talk about some of the major ones.
Use Cases of FLAC
- Streaming music: For music enthusiasts, FLAC is a widely used format for recording or listening to high-quality audio without taking up too much storage space. Thanks to its lossless compression techniques, FLAC offers an ideal solution for those with such requirements.
- Music/audio production: DJs and producers also benefit from using FLAC files, as the lossless format allows them to collaborate and share audio files with each other without compromising quality. For this reason, FLAC has become the preferred format for most of their needs.
- Archiving digital audio: The FLAC format is perfect for archiving rare, unique, and historical audio recordings. Its ability to preserve digital audio over the long term without any loss of quality makes it an excellent choice for efficiently storing and preserving these valuable recordings.
Use Cases of WAV
- Professional Audio Applications: WAV is the industry standard audio format for professional purposes such as sound recording and editing. Since the files are uncompressed, all of the original elements and data in the audio are preserved, resulting in high-fidelity sound.
- Video Production: The uncompressed nature of WAV files ensures that the audio is consistent across different devices while also allowing smooth syncing with the video footage. As such, video producers use WAV files for their requirements.
- Audio Mastering: WAV files are used for the ultimate stage of audio mastering. The main purpose is to create the highest-quality master recording that can further be duplicated and distributed to the masses.
How to Convert FLAC to WAV or WAV to FLAC?
Here are several methods to convert between FLAC and WAV:
1. Using Dedicated Audio Conversion Software:
Audacity:
- A powerful, open-source audio editor.
- Import your FLAC or WAV file, select "Export Audio," and choose the desired format.
2. Using Online Conversion Tools:
Websites like Zamzar or Online Audio Converter let you convert FLAC to WAV (or WAV to FLAC) without installing any software. However, keep in mind there might be file size limits for larger audio files.
3. Using Media Players:
VLC Media Player:
- Open the desired file in VLC.
- Go to "Media" -> "Convert/Save."
- Choose the input file, select the output format (WAV or FLAC), and start the conversion process.
4. FFmpeg:
Use the following command to convert FLAC to WAV:
ffmpeg -i input.flac output.wav
To convert WAV to FLAC:
ffmpeg -i input.wav output.flac
Conclusion
Both FLAC and WAV audio file formats offer high-quality sound, but they differ in terms of file size, compatibility, and usage. When choosing between the two, it's important to weigh their respective merits and demerits. By understanding the differences between FLAC and WAV, you can make an informed decision and get the best out of your audio experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is WAV the highest-quality audio format?
No, WAV is not necessarily the audio format providing the highest quality files. This depends on a lot of factors like bit depth, sample rate, and compression levels. As such, FLAC files can rival the quality provided by WAV.
2. Is there a quality reduction when you convert WAV to FLAC?
As FLAC is a lossless compression format, there is no data or quality loss when WAV files are converted to FLAC files.
3. Why does FLAC sound better?
FLAC can sound better than WAV files in some cases because it uses the lossless compression technique. Therefore, it can offer better apparent sound quality while consuming less storage space in comparison to WAV files.
4. Is Spotify using FLAC or WAV?
Spotify uses Ogg Vorbis format for streaming, not FLAC or WAV, to balance audio quality and file size.
5. Is WAV lossless?
Yes, WAV is lossless because it is an uncompressed audio file format. As such, there is no data or quality loss.