What is M4A?
M4A is a file extension used for audio files that are encoded with the Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) codec. It is a common format for storing audio content, particularly music, podcasts, and other audio recordings. M4A files are noted for their high-quality sound and efficient compression, allowing for reduced file sizes without significantly reducing audio fidelity. They are compatible with a wide range of devices and media players, making them the best option for distributing and sharing audio content online.
Pros and Cons of M4A
Pros:
- The AAC codec used in M4A files compresses effectively, allowing for reduced file sizes while preserving high audio quality. This is useful for optimizing storage space and streaming content online.
- M4A files can store metadata such as the artist's name, album title, track number, and cover art, making it simple to organize and manage audio files with additional information.
Cons:
- While M4A provides good audio quality with effective compression, it is not appropriate for storing lossless audio formats like FLAC or WAV, which may be preferable in some professional or audiophile applications.
- Converting M4A files to other audio formats, or vice versa, can occasionally result in quality loss or compatibility concerns, especially if the conversion is not done correctly.
What is MP3?
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer III) is a common audio compression format for digital audio. It is one of the most widely recognized and commonly used audio formats for digitally storing and transmitting music and other audio recordings. MP3 files use lossy compression to minimize file size while keeping audio quality, making them suited for a wide range of applications like music streaming, downloading, and portable device listening. MP3 files are compatible with a wide number of devices, media players, and software.
Pros and Cons of MP3
Pros:
- MP3 is widely used for streaming music and downloading audio files from the internet. Its small file size enables smoother streaming, even with limited internet bandwidth.
- At larger bitrates (such as 320 kbps), the decrease in sound quality from compression is frequently insignificant.
Cons:
- Compared to lossless audio codecs such as FLAC or WAV, MP3 files have lower audio fidelity, particularly at lower bitrates. This can cause obvious artifacts, such as compression artifacts or reduced dynamic range, especially in heavily compressed MP3 files.
- The MP3 format was created using patents, and some parts of its encoding and decoding operations may need licensing payments. This might provide difficulties for software developers and manufacturers attempting to include MP3 support in their products. However, several patents relating to MP3 technology have expired or become more widely available over time.
Difference Between MP3 and M4A
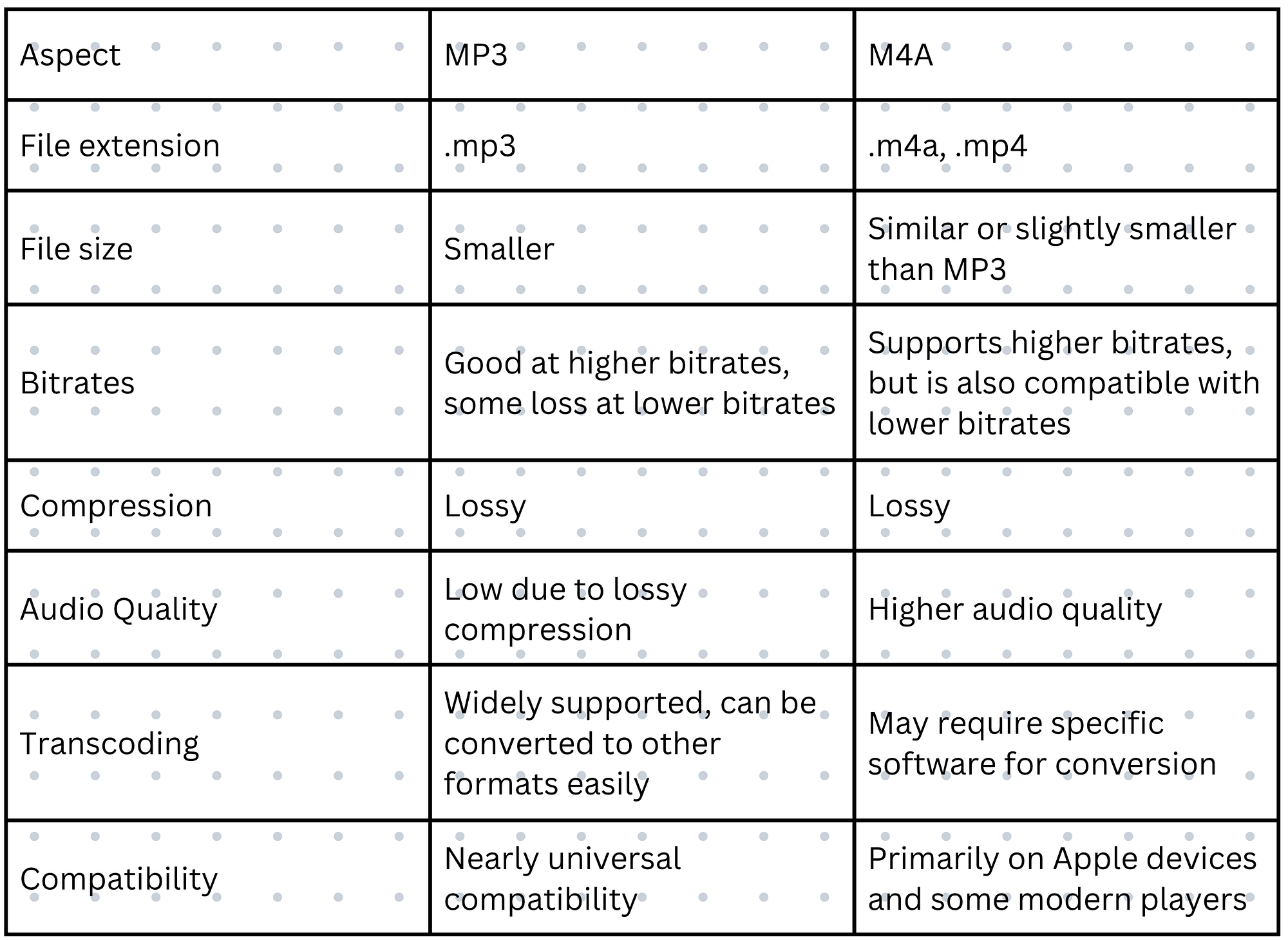
Bitrates
Both MP3 and M4A use variable bitrates, which means the file size varies depending on the audio quality selected. M4A, on the other hand, frequently achieves comparable or significantly higher sound quality than MP3 at the same bitrate. This is because M4A often employs a more advanced compression method (AAC), which can be more effective in preserving audio fidelity.
Audio Quality
MP3, using lossy compression, sacrifices some audio data to reduce file size, leading to potential loss of clarity and detail, especially noticeable at lower bitrates. On the other hand, M4A, utilizing the AAC codec, offers higher audio quality even at lower bitrates, resulting in better sound fidelity and less noticeable artifacts. This makes M4A preferable for those prioritizing audio quality, while MP3 remains popular for its smaller file sizes and widespread compatibility.
Transcoding
Due to its widespread use, most devices and software can convert MP3s to other formats readily. When transcoding MP3 files between different formats or bitrates, there is a higher risk of additional audio data loss, leading to a noticeable degradation in audio quality over successive conversions. M4A, on the other hand, might require specific software for conversion, especially on non-Apple devices, as its AAC encoding isn't universally supported for transcoding.
Compatibility
MP3 is widely compatible with a variety of devices, media players, and software systems. It is a standard format supported by almost all modern devices, making it simple to distribute and play MP3 files without encountering compatibility concerns. M4A, while essentially superior in quality, is primarily supported by Apple devices and some newer media players. It may have limited support for some older or less popular platforms, necessitating the use of extra plugins or software updates for smooth playback.
Common Use Cases for M4A and MP3 Audio Formats
Here are some common applications for MP3:
- Online Music Distribution: Many music streaming platforms and online music stores use MP3 for distributing music due to its small file sizes and widespread support. MP3 files can be easily downloaded, streamed, and shared, making them a popular choice for digital music distribution.
- Universal Music Playback: MP3 is widely used for playing music across a broad range of devices. Its broad compatibility and small file sizes make it ideal for storing and playing large music collections without consuming excessive storage space.
Here are some common applications for M4A:
- Podcasts and Audiobooks: M4A is also commonly used for distributing podcasts and audiobooks due to its ability to maintain good audio quality while keeping file sizes relatively small. Content creators appreciate M4A for delivering clear voice recordings without sacrificing too much storage space.
- Professional Audio Production: In professional audio production environments, M4A is often used to store master recordings and high-quality audio files. Its support for metadata and better audio quality compared to MP3 makes it suitable for archival purposes and exchanging audio files among professionals.
How to convert M4A to MP3 and vice versa?
There are various tools available for converting M4A to MP3, including:
- CloudConvert
- Restream
- Convertio
To convert M4A to MP3 or vice versa using CloudConvert, follow these steps:
- Head to the website and click "Select Files" to choose the M4A file(s) you want to convert. You can also drag and drop the files directly into the browser window.
- In the conversion options, select “MP3” as the output format. Then, click the "Start Conversion" button to initiate the process.
- After conversion, CloudConvert allows you to download the resulting MP3 file(s) or save them to various cloud storage services like Dropbox or Google Drive.
FAQs:
- Does M4A lose quality?
M4A generally maintains good quality, but at lower bitrates, there may be some loss compared to higher-quality formats.
- Are there any differences in the encoding process between M4A and MP3?
Yes, M4A uses the AAC codec, while MP3 uses the MPEG Audio Layer III codec.
- Should I convert MP3 to M4A?
Converting MP3 to M4A may not significantly improve quality since it involves lossy compression. MP3 is widely compatible, convert M4A if needing compatibility with Apple devices.
- What is the best quality music format?
The best quality music format depends on various factors, but lossless formats like FLAC and WAV offer the highest audio fidelity, while M4A and MP3 are suitable for general listening with acceptable quality.