MKV and MP4 are two of the more popular video formats. As a result, there is often confusion as to which of the formats is better and which should be preferred when. To truly understand the differences between the two, it is crucial to understand what each of these formats offers and how they differ from one another. To help you understand that, let’s use this article to talk about MKV and MP4 file formats and how they differ!
What is MKV?
MKV, also known as Matroska Video Files, is one of the most basic video formats, and the lead developers of Matroska originated it. It is an open-source video format and allows for all kinds of different audio-visual content to be packed inside the format. As a result, an MKV file can hole different audio tracks, video tracks, and subtitle files - thereby facilitating smoother sharing and distribution of these files. The name is derived from the famous Russian Matroska dolls wherein different-sized dolls were inserted, one inside the other.
A single MKV file is powerful enough to host a movie with audio in multiple languages and respective subtitles for the user to pick the relevant audio and subtitle format while viewing the video. This feature makes the MKV format extremely useful.
Pros of MKV:
- Supports a wide range of codecs, subtitles, and metadata, making it highly adaptable for various media types.
- Can store high-quality video and audio streams without much compression loss, suitable for HD and 4K videos.
Cons of MKV:
- Less optimized for streaming compared to MP4, requiring more bandwidth.
- Not as widely supported on mobile devices and older hardware without third-party software.
Schedule a Demo with Our Video Expert!
Discover how Gumlet can help you build a cutting-edge video streaming infrastructure.
What is MP4?
MP4 was created by the Moving Pictures Expert Group as their standard video coding format and was released back in 1998. Currently, there are over two dozen different MPEGs. This is one of the most commonly used container file formats and is used for Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP, and is also compatible with Apple’s HLS streaming.
The MP4 format is based on the MPEG-4 Part 12, which is based on the QuickTime File Format. Like MKV, the MP4 format, too, supports an array of codecs - most commonly H.265 or H.264 for video and AAC for audio. Because of the sheer versatility in its application, MP4 has widely grown to be one of the most utilized video containers capable of delivering both MPEG-DASH and HLS - two top streaming protocols.
Pros of MP4:
- Balances file size and quality effectively, ideal for sharing and streaming.
- Easier to edit and convert using a wide range of video editing tools.
Difference Between MKV vs MP4
With the basics of MKV and MP4 in place, let’s now move toward some important points of difference between the two. Here is a comparison table that gives you a quick overview of some important points of difference between MKV and MP4. Post that, we will talk about the two formats and how they differ based on different important parameters.
| Feature | MKV | MP4 |
|---|---|---|
| File extension | .mkv | .mp4 |
| File Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Quality | Potentially higher | Generally lower |
| Video and Audio Codecs Supported | Wide range (H.264, H.265, VP9, AV1, FLAC, etc) | More limited (H.264, H.265, AAC, etc.) |
| Compression | Less efficient | More efficient |
| Compatibility | Less widespread | More widespread |
| Subtitles | Supports advanced subtitles (e.g., ASS, SSA) | Basic subtitle support (e.g., SRT, VTT) |
| Editing | More complex | Simpler |
| Licensing | Open source | Proprietary: may involve licensing fees |
| Metadata Support | Extensive | Limited |
| Common Use Case | High-quality videos, multiple tracks, archiving | General-purpose video, streaming, mobile devices |
Video Quality
MKV vs. MP4 - which video format is responsible for producing better-quality videos? Well, this is an obvious question, but it does not have any answer that is set in stone, to be honest. The final quality of the file that you receive depends entirely on the codecs that you are using in your container and not the container format itself. So, while both MKV and MP4 are containers, the final quality that they will produce will depend on the codecs that you are packing with each format. So, if you use both MKV and MP4 with the same audio and video codecs, you will find the quality of the two to be similar.
File Size
Again, when it comes to comparing MKV vs. MP4 based on their file size, it should be noted that these two are just container formats, and the final file size is determined by the video bitrate and the codecs being used to encode audio and video. If you use the same codecs and the same bitrate, you will find that the file sizes of MKV and MP4 are both comparable. However, MKV is generally larger than MP4 as it supports additional features, subtitle files, multiple language audio support, and so on. However, if you have an MKV video file that is smaller in size than MP4 despite being of higher resolution, it can be because of more advanced codecs used with MKV as compared to MP4.
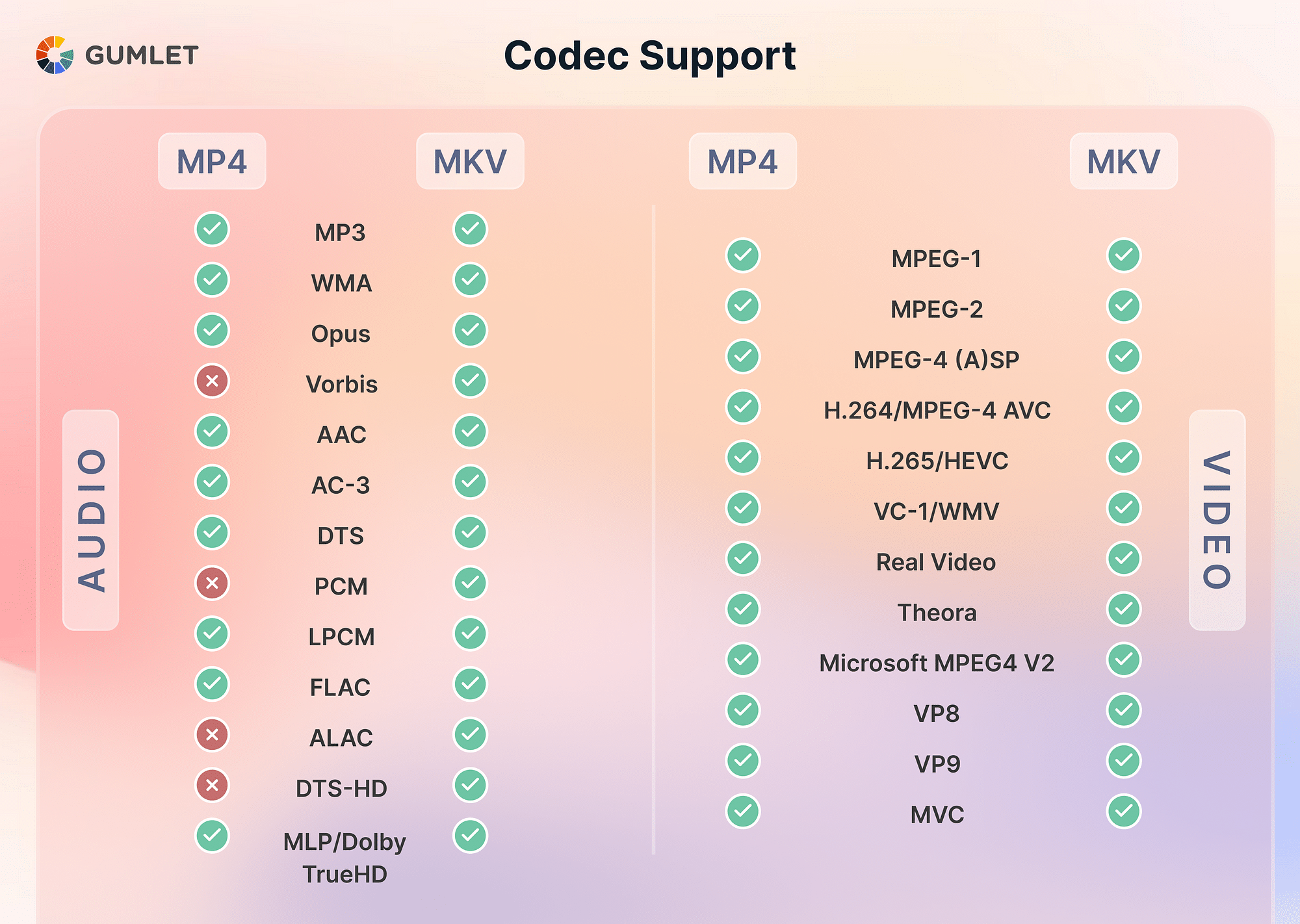
Video and Audio Codecs Supported
As we mentioned earlier, the MKV format can store unlimited multimedia content, ranging from subtitles, audio, videos, and more. As a result of this, the MKV format is commonly used for TV shows and movies. It supports all audio-visual encoding formats, some of which even MP4 doesn’t support, which makes it a good format for streaming movies and so on.
Both MKV and MP4 can be encoded using the HEVC video codec supporting UHD resolution. However, one prime difference between MKV and MP4 is that MKV supports FLAC, whereas MP4 doesn’t. This makes MKV a much better format for lossless digital audio compression.
Platforms Compatibility
MKV format supports multiple video/audio language tracks as well as subtitle files, making it an ideal format for HD movies/TV shows, as well as for streaming things in a foreign language. MKV is compatible with most mainstream media players and video editing tools like VLC, KMPlayer, Adobe PremierPro, and so on.
Compared with MKV, the MP4 format has much wider compatibility and can run on literally any operating system or device. So, in terms of platform compatibility, MP4 wins over MKV, hands down.
MKV vs MP4: Which is Better?
MP4 is generally better for video streaming because it offers more efficient compression, better compatibility with most devices, and easier streaming from multiple sources compared to MKV. MP4 is a more widely supported format, and the files are usually much smaller in size than MKV files, making them easier to stream. MP4 also has more significant support for DRM (Digital Rights Management), so you can use it to protect your content from unauthorized access. For live streaming also, MP4 is generally a better choice as it is more widely supported and provides better compression.
How to Convert MKV to MP4 and MP4 to MKV?
To convert an MKV file to MP4, you can use ffmpeg with a simple command. If the codecs in the MKV file are supported by MP4, this process can be very fast as it doesn't re-encode the streams (remixing).
ffmpeg -i input.mkv -c copy output.mp4If the codecs are not compatible, you need to re-encode:
ffmpeg -i input.mkv -vcodec libx264 -acodec aac output.mp4Similarly, to convert MP4 to MKV, you can remux the file or re-encode it depending on your needs.
Remux Command (No Re-encoding):
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -c copy output.mkv
Re-encode Command (For Compatibility):
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vcodec libx264 -acodec aac output.mkv
Conclusion
Clearly, there is no clear winner between the two, and the answer to the question - “Which is better out of MKV and MP4” will depend heavily on what you plan on doing with your video formats. We hope this article helped you draw out the key differences between the two formats and resolved any confusion that you might have had regarding the same!
FAQs
- Which media players support MKV and MP4?
MKV is supported by VLC Media Player, KMPlayer, Plex, Kodi, and PotPlayer.
MP4 is universally supported by almost all media players, including VLC, Windows Media Player, QuickTime, and smartphones.
2. Does MKV to MP4 reduce quality?
No, MKV to MP4 conversion does not reduce quality. The quality of the file depends on the resolution and bitrate of the original file. If the original file is high quality, then the converted file will also be high quality.
3. Is MKV or MP4 better for Youtube?
MP4 is the preferred video format for YouTube as it is the most compatible format. YouTube does not support MKV files, so if you want to upload a video to YouTube, you should convert it to MP4 first.
4. Is an MKV file lossless?
No, MKV files are not lossless. MKV files are a container format that can support various audio and video codecs. Lossless audio formats, such as FLAC or ALAC, can be stored in an MKV file, but they are not the same.