Introduction - Video Resolution and Pixels
Video resolution is a major determinant of video quality. It represents the ability of video recording devices to capture the smallest individual element (detail) of an image—which is the pixel. The number of pixels on a screen is equivalent to the resolution of that screen. The higher the number of pixels, the greater the detail and clarity of a picture.
At higher resolutions, you can see the details of the image more clearly and hence, can edit and manipulate it with greater ease.
Among the common video resolutions are 720 x 480, 1280 x 720, 1920 x 1080, and 3480 x 2160.
You will notice that resolutions are often followed by “p” or “i”. For instance, 1080p and 1080i. This essentially refers to how an image is scanned. The “p” refers to “progressive scanning," and “i” refers to an “interlaced" image. While the former produces better video quality, the latter is easier to broadcast.
We'll discuss these terms in later sections.
What is SD?
As is evident from its name, SD or Standard Definition refers to the standard or base level resolution for streaming—which is 480 pixels in a single image. While it is technically possible to stream at lower resolutions like 144p, 240p, and 360p, SD has been used as an acceptable resolution in the world of live streaming for many years now.
You will find that SD resolution is commonly used in digital cameras, camcorders, and even for some TV broadcasts. For instance, in the American NTSC system, videos with an aspect ratio of 4:3 only have 480i available.
SD videos have lower definitions and tend to be blurry videos. Depending on the availability of bitrates, SD video quality becomes lower. However, this works as an advantage where less-than-optimal internet connectivity is concerned. You can still reliably stream videos without worrying about buffering and lags.
What is HD?
HD, or High Definition, is a resolution of 720 or 1080 pixels, commonly used for internet playback streaming. Standard HD is best suited for regular live streaming, while Full HD is used for higher-quality videos. HD provides greater clarity and definition due to less pixelation, superior color reproduction, and faster frame rate.
However, it requires significantly higher internet bandwidth, causing dropouts and stuttered streams. HD streams also demand 4x more data and require more power, which can affect device battery life, especially if using outdated editing software or computers. In short, HD offers a smoother and higher definition streaming experience, but it also requires higher internet bandwidth, storage capacity, and power consumption, which can impact device battery life.
Types of Video Quality
In practice, we have four primary video resolutions: 360p, 480p, 720p, and 1080p — which represent the number of horizontal lines on a video. Anything beyond 1080p is Ultra HD or 2160p or 4k. As is evident, the higher the resolution, the higher will the quality of your video be.
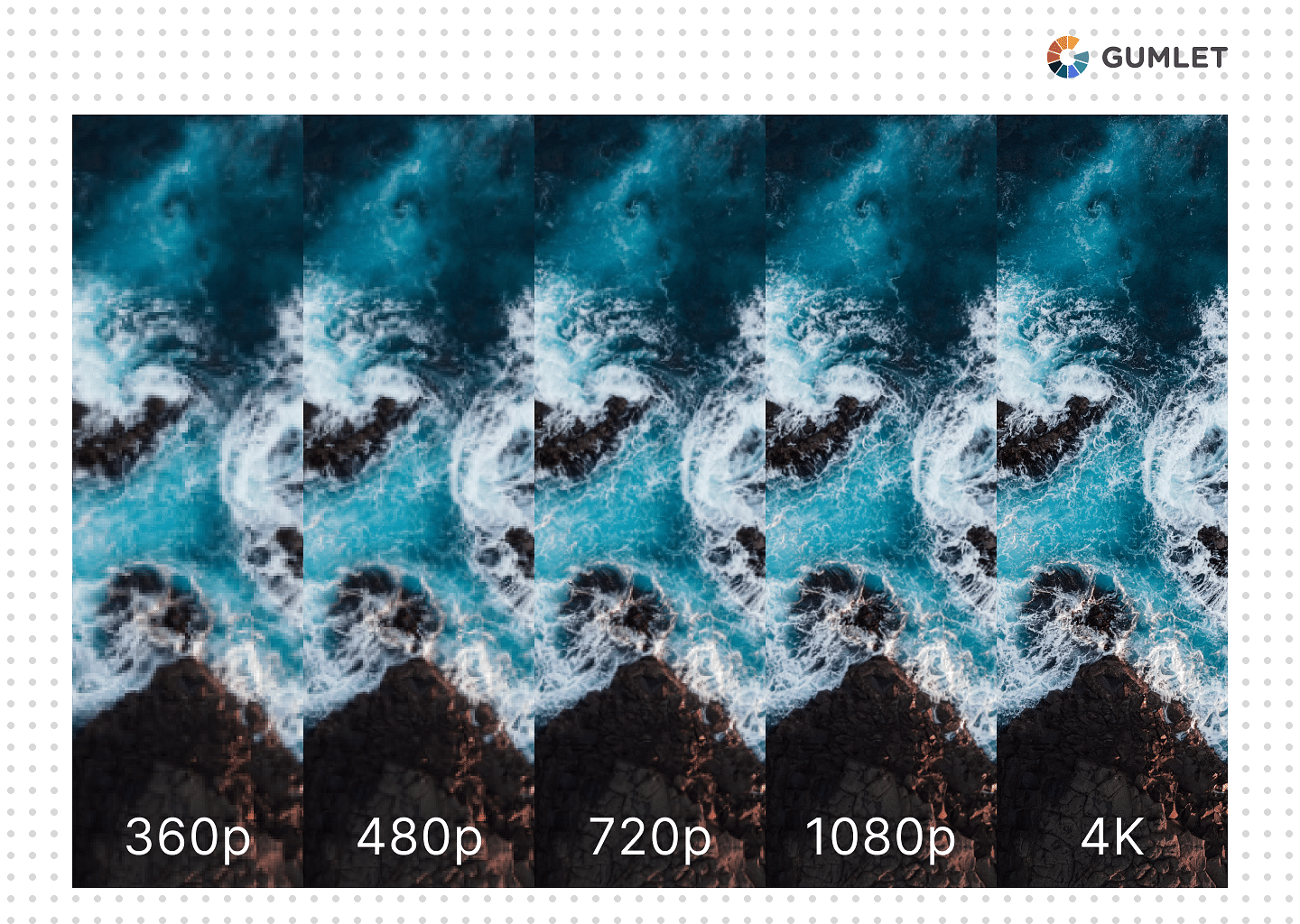
Here's exploring the different types of video resolution formats in detail.
| Resolution | Common Name | Pixel Dimensions | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4K | Ultra HD (UHD) | 3840 x 2160 | 16:9 |
| 1080p | Full HD (FHD) | 1920 x 1080 | 16:9 |
| 720p | HD | 1280 x 720 | 16:9 |
| 480p | Standard Definition (SD) | 854 x 480 | 16:9 |
| 360p | Low Resolution | 640 x 360 | 16:9 |
| 240p | Very Low Resolution | 426 x 240 | 16:9 |
360p - LD - Low Definition
Most of the YouTube content you see will be marked 360p, which indicates the lowest resolution that a video can be streamed in wherein the picture quality is not blurry or unclear. 360p is best suited for smartphones since the smaller screens do not highlight the blurry quality of the video as noticeable when compared to larger screens.
480p - SD - Standard Definition
480p is a widely accepted standard or cut-off for SD videos, wherein the 480 refers to a pixel height of 480 in a single image, and "p" refers to images being transmitted as a progressive scan. 480p provides decent image quality without buffering or lags even if you have a poor internet connection.
720p - HD - High Definition
720p format, with a resolution of 1280x720 pixels, is commonly used for internet streaming videos. It offers progressive HDTV scanning with 720 horizontal lines/1080 columns and a 16:9 video aspect ratio. While 1080p videos have better clarity and smoother motion, 720p has 921,600 pixels, while 1080i or 1080p images have up to 2 million pixels. 720p is less demanding on bandwidth and power due to its progressive scan transmission.
1080 and 1080i - FHD - Full High Definition
1080p, or Full-HD, is a display resolution of 1920x1080 with 1,920 pixels horizontally and 1,080 pixels vertically. It uses a progressive scan, producing higher picture quality, as each frame is drawn in a single pass. 1080i, on the other hand, is an interlaced scan image, drawing every frame in two passes across the screen. Both have a 16:9 video aspect ratio, but 1080i takes slightly longer for the human eye to see a complete frame. 1080p is used for HD broadcasts, Blu-ray players, and Xbox/PlayStation games, while 1080i is used for interlaced HD images.
2160p - 4k or UHD - Ultra High Definition
Ultra High Definition (UHD) has a display resolution of 3,840 x 2,160, four times the full HD resolution of 1080. It represents 2160 pixels across the shorter side of the screen and is often used as an alternative name for 4k. UHD images are smoother and carry more detail than full HD images, but 1080p images may appear blurry around the edges and written text may be less clear.
Beyond 4k
Further in advanced display technology, we have 8K, which refers to a display resolution format of 7680 x 4320 i.e., 4 times a UHD resolution (4k) and 16 times a full HD resolution (1080). This technology eliminates pixelation, resulting in pixel-less images and superior picture quality. However, 8K requires higher bandwidth, connectivity, and transfer speed configurations, which may require upgrading TVs and other devices. Video content creators are yet to produce large-scale 8k content for broadcasters to adopt.
Difference between HD and SD
| Aspect | SD (Standard Definition) | HD (High Definition) |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 480p or lower | 720p, 1080p |
| Picture Quality | Lower quality, less sharp, visible pixelation on large screens | Crisp, clear images with finer detail, better for larger screens |
| File Size | Smaller file size, easier to download or stream | Larger file size due to higher resolution |
| Bandwidth | Requires less bandwidth, ideal for slower internet | Requires more bandwidth but offers superior quality |
| Storage Space | Takes up less space | Requires more storage space due to higher resolution |
| Compatibility | Compatible with older devices | Compatible with most modern devices |
| Streaming | Suitable for slow internet speeds | Better for fast internet connections |
| Viewing Experience | Less immersive, suitable for smaller screens | More immersive, better for larger screens |
Video Quality
SD is associated with a lower-quality streaming experience wherein the maximum resolution is 480p. Even though 480p carries more detail and information than a 360p, 240p, or 144p image, it isn't the best option if you are looking for a top-notch streaming experience. HD streaming clearly wins here by ensuring superior image quality, better colors, clarity, detail, and definition. For this reason, it is worth making the extra investment and opting for HD streaming.
Bandwidth Consumption
As is understood, HD streaming requires more bandwidth since you need to stream at a higher bitrate. To give you an idea of where HD vs SD streaming is concerned, you require an internet speed of roughly 25 Mbps and higher to stream 1080p HD videos, at least 10 Mbps for 720p videos, and 5 Mbps for 480p video.
If your target audience is likely to have notoriously poor internet speeds, you don't have much of a choice. However, SD is likely to fizzle out over the next few years as mobile devices and video streaming technology are progressively moving beyond the SD norms.
Video File Size
Higher resolution also translates to bigger file size, greater storage capacity, and processing power requirements. This could be a disadvantage for you if you are still working with older, low-capacity devices and outdated technology (or need to share a file over a slow connection).
Is HD or SD better?
HD is generally better than SD due to its superior resolution, providing clearer, more detailed visuals and a better overall viewing experience. For streaming, HD is ideal, especially on larger screens. However, SD is still useful in low-bandwidth situations. Fortunately, Gumlet offers a cutting-edge streaming platform that automatically optimizes video quality based on bandwidth and processing power. It also allows users to manually select their preferred resolution, offering flexibility for those who want to override default settings for a customized experience.
Common Applications for SD
- Video Surveillance Systems: Due to the need for continuous recording and the potential for multiple cameras, SD is often used in security systems to reduce storage requirements and bandwidth consumption.
- Web Conferencing and Video Calls: For users with slower internet connections or older hardware, SD can provide a more stable and reliable video conferencing experience.
Common Applications for HD
- Movies and Television: Most modern movies and TV shows are produced and distributed in HD, providing a more immersive and detailed viewing experience.
- Video Games: Many video games now support HD resolutions, offering improved graphics and visual fidelity.
UHD vs HD vs SD: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | SD (Standard Definition) | HD (High Definition) | UHD (Ultra High Definition) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 720 x 480 (480p) | 1280 x 720 (720p) | 3840 x 2160 (4K) |
| Aspect Ratio | 4:3 or 16:9 | 16:9 | 16:9 |
| Pixel Count | ~ 0.3 Megapixels | ~ 1 Megapixel | ~ 8.3 Megapixels |
| Visual Clarity | Lower clarity | Clearer, more detailed | Extremely detailed, sharper |
| Bandwidth | Lower bandwidth required | Moderate bandwidth required | Higher bandwidth required |
| Viewing Distance | Best viewed close-up | Optimal at medium distance | Optimal at greater distances |
Conclusion
Now that you are aware of the nuanced differences between HD and SD resolution formats, you can make an informed choice for your different video streaming requirements. It's always recommended to experiment with multiple formats to get better clarity on the advantages and disadvantages of HD and SD wrt to your projects.
FAQs
- Is SD bigger than HD?
No, HD (High Definition) has a higher resolution than SD (Standard Definition), meaning HD files typically contain more pixels and detail.
- Is SD stream faster than HD?
SD is the standard definition at which viewers can comfortably stream videos despite a poor internet connection. It requires less bandwidth and storage capacity. However, HD streams have higher picture quality and detail, which results in a better streaming experience. If you can afford an upload speed of 2.5 Mbps or higher, it is recommended that you go with 720p.
- What is the difference between SD HD and 4K?
SD typically has a resolution of 480p, HD ranges from 720p to 1080p, and 4K offers about four times the resolution of 1080p, providing much sharper images.
- Is SD still relevant?
Yes, SD is still relevant in some niche applications, such as older TVs, security cameras, and streaming services for users with limited bandwidth.
- How do streaming services handle SD and HD content?
Streaming services often offer both SD and HD options, automatically adjusting quality based on the user’s internet speed and device capabilities.
- Does SD or HD use more data?
HD uses significantly more data than SD due to its higher resolution and quality, making it less suitable for limited data plans.