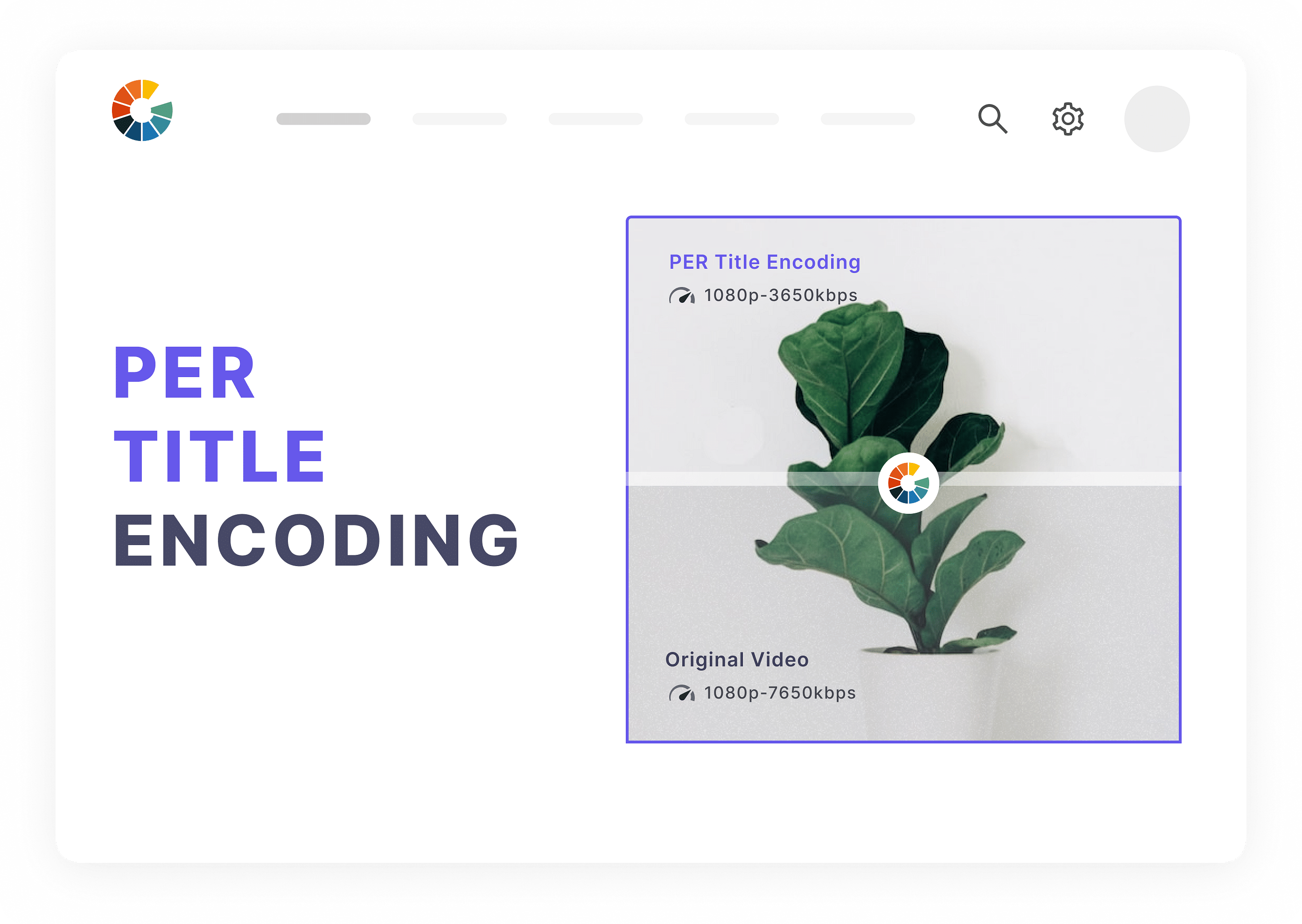
Encoding is basically the process of compressing raw video into a format that is compatible with different platforms and devices. Transcoding, on the other hand, takes compressed video files, decodes and modifies its key attributes—bit rate, video size, etc—and re-encodes it again to ensure seamless video transmission to a geographically dispersed audience.
Transcoding is the best option if you need to convert a video file to a different format. It helps optimize your video or audio files for different devices, browsers, or streaming services. Encoding is the best option if you are looking to compress the video for faster streaming or downloading. To decide which is the right one for you, you will need to understand each of these and their differences in detail.
Video Encoding Basics
The most common reason to encode video is to compress it so that it takes up less space, making it easier to store and distribute. Video encoding can also be used to convert video from one standard to another (e.g., PAL to NTSC), or to change the format of the data so that it can be played on a different type of device (e.g., a DVD player).
There are two main types of video encoding: lossy and lossless. Lossy encoding involves throwing away some of the video data in order to achieve a smaller file size. This means that the encoded video will not be an exact copy of the original, and there will be some degradation in quality. Lossless encoding, on the other hand, keeps all of the original data intact, resulting in a larger file size but no loss of quality.
The most common video codecs used for encoding are H.264 and H.265. These codecs are used by Blu-ray discs, DVDs, and many online video streaming services. Each codec uses a different algorithm for compressing data, so the choice of the codec will impact the quality and file size of the encoded video. Learn more about H.264 vs. H.265.
When encoding video, it is important to strike a balance between quality and file size. A smaller file size will result in lower quality, but a larger file size will take up more storage space and be more difficult to distribute. The best way to find the right balance is to experiment with different settings and compare the results.
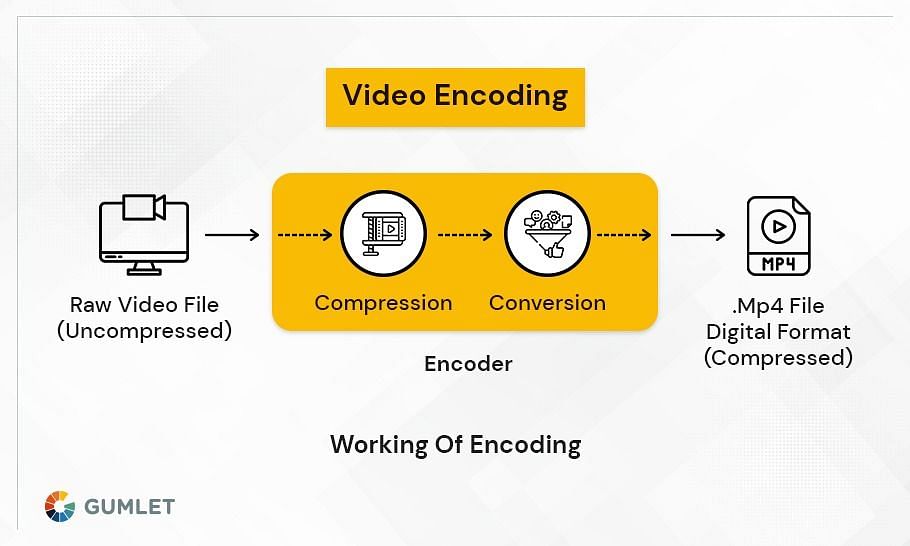
Does Encoding Video Reduce Quality?
Video encoding is one of the most important factors in determining video quality. The way a video is encoded can have a significant impact on both the file size and the overall quality of the video. There are a number of different video encoders available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a video encoder, it is important to consider the desired output format, file size, and quality.
One of the most popular video encoders is H.264, which is commonly used for Blu-ray discs and HDTV broadcasts. H.264 offers very high levels of compression, meaning that it can reduce the file size of a video without sacrificing too much quality. However, H.264 can be computationally intensive, so it is not always the best choice for low-end devices.
Another popular video encoder is MPEG-4, which is often used for streaming video on the internet. MPEG-4 offers a good compromise between file size and quality, so it is a good choice for many applications. However, MPEG-4 can be less compatible with some devices, so it is important to check compatibility before using this format.
The final major video encoder is VP8, which was developed by Google. VP8 offers very high levels of video compression but at the expense of some quality. VP8 is a good choice for applications where file size is more important than quality, such as in web videos. However, VP8 is not as widely compatible as other video encoders, so it is important to check compatibility before using this format.
Video Transcoding Basics
Video transcoding is the process of converting video from one format to another. This can be done for a number of reasons, such as to improve compatibility with a particular player or device, to reduce file size, or to change the resolution or quality of the video.
There are a number of different software programs that can be used for transcoding, and the specific steps involved will vary depending on the program being used. However, in general, the process usually involves selecting the input video file, choosing the desired output format and settings, and then starting the conversion process.
One of the most important things to keep in mind when transcoding video is that it can be very easy to lose quality in the process. For this reason, it is often best to start with a high-quality input file, and then use the lowest possible settings when creating the output file. This will help to ensure that the final video is as close to the original as possible.
When transcoding video, it is also important to be aware of any potential copyright issues. Some formats, such as MPEG-2, are protected by patents and can only be used for personal use. Others, such as H.264, are open standards and can be used without restriction. Be sure to check the terms of use for any software you plan on using before starting the transcoding process.
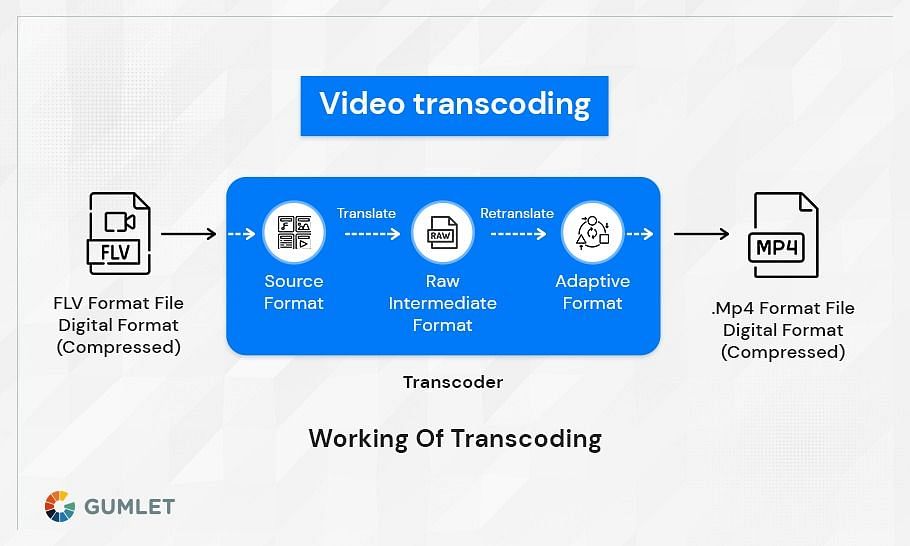
Does Transcoding Video Reduce Quality?
Transcoding is the direct digital-to-digital conversion of one encoding format to another. This process typically happens when content needs to be played on a device or platform that doesn't support the original encoding format. For example, converting an AVI file to an MP4 file. Since transcoding involves re-encoding the video, it will likely result in some loss of quality. The degree of quality loss will depend on a number of factors, including the codecs used and the settings used during the transcoding process. In general, though, you can expect some degradation in video quality when transcoding.
Key Difference Between Encoding and Transcoding
| Encoding | Transcoding |
|---|---|
| The process of compressing digital media file to reduce file size. | The process of converting a digital media file from one encoded format into another |
| Typically used for compression | Typically used for making encoded video compatible with more than one device. |
| It is usually done once. | It can be done multiple times depending on the final video destination |
| Does not change the resolution or aspect ratio of the video | Can change the resolution or aspect ratio of the video |
| Encoding typically takes less time than transcoding, as it does not need to decode and recompress the data. | Transcoding takes more time to decode and recompress the data into a required format. |
| It is usually done at the start of the video workflow. | Transcoding is done later in the video workflow process. |
Encoding is done when you need to convert video into smaller, more manageable sizes. It allows you to compress video files worth in gigabytes into megabytes to improve its delivery to an online audience.
Encoding is an indispensable process in streaming video—without which delivering video streams would be next to impossible.
However, that's not necessarily the case with transcoding—which is typically dependent on the audience streaming the footage. For example, if you are streaming live content from a private network using on-site tools and devices, you wouldn't need to transcode video.
However, if your audience is broad, geographically-dispersed, streams videos using different devices and media players, and has varying network conditions, it's imperative to transcode videos to ensure playback compatibility.
Similarities Between Encoding and Transcoding
Both transcoding and encoding serve crucial purposes in making video streaming accessible and disruption-free. The processes are essentially designed to improve playback compatibility with different platforms, media players, and devices.
However, despite their common purposes, they don't share similarities and have extremely different processes.
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped to understand the basics of transcoding and encoding and their importance in seamless and secure content delivery.
If you are looking to purchase a fully-managed video encoding and transcoding software for your enterprise, Gumlet is a top-grade solution that is purpose-built to automate your video publishing pipelines. Gumlet's intuitive infrastructure uses multi-CDN rerouting to ensure 99% uptime and effectively reduces latency and re-buffering across different platforms.