Today, video content reigns supreme. From streaming movies and TV shows to attending virtual meetings, video is an integral part of our lives. To deliver this content seamlessly, efficient video compression is essential. Enter VP9, an open-source video codec that has revolutionized how we experience video.
What is VP9 Codec?
VP9 is an open-source video codec developed by Google after their acquisition of On2Technologies in Feb 2010. This was the second codec, after VP8, to be released, and it became available to the masses in June 2013.
It's designed to deliver high-quality video at lower bit rates than other codecs. This makes it particularly efficient for streaming video over the internet. In terms of usage, the largest distributor of VP9-codec content was YouTube. Later, in 2016, Netflix, too, announced the use of VP9 for their platform. Since then, many new use cases have emerged where VP9 has proven to be a viable solution.
VP9 Codec Specs
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Type | Open-source video codec |
| Container Formats | WebM, Matroska |
| Bit Rate | Flexible, supports a range of bitrates for different quality and bandwidth needs |
| Bit Depth | 8, 10, 12 bits |
| Resolution Support | Up to 8K |
| Supported Media Players | VLC, MPlayer/MPlayer2/MPV, Kodi, MythTV, FFplay |
| Frame Rates | Flexible, supports high frame rates |
| Supported Devices | Wide range of devices |
| Profiles and Levels | Multiple profiles and levels for different device capabilities |
| Browser Support | Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Safari, Opera |
Key Features and Benefits of VP9
- Open Source: VP9 is free to use, alter, and distribute without requiring royalties to be paid.
- High compression efficiency: Saves bandwidth by delivering excellent video quality at lower bitrates.
- Wide Support: Compatible with a large number of devices, operating systems, and web browsers.
- Performance: VP9 outperforms other codecs in terms of bitrate efficiency and video quality. However, performance can vary depending on factors like content type, encoding parameters, and hardware capabilities.
How does VP9 codec work?
VP9's architecture consists of several key components:
- Frame Structure: The video is segmented into frames, which are then broken down into macroblocks.
- Prediction Modes: VP9 uses different prediction techniques to minimize redundancy between frames.
- Transform and Quantization: The video data is converted into frequency coefficients and then quantized to reduce accuracy.
- Loop Filter: Enhances image quality by minimizing blocking artifacts.
- Rate Control: Regulates the bitrate to strike a balance between video quality and file size.
How VP9 Achieves High Compression
VP9 achieves high compression efficiency through various means:
- Sophisticated Prediction Modes: Effective prediction of video content reduces the data required to encode the differences.
- Efficient Transform and Quantization: Improved techniques for transformation and quantization help minimize data loss.
- Adaptive Loop Filter: The loop filter adjusts its settings dynamically based on the video's content.
- Smart Rate Control: Allocates bits intelligently across different parts of the video to ensure consistent quality.
VP9 Comparison with Other Video Codecs
VP8 vs VP9
VP8 and VP9 are both video codecs developed by Google, but they differ significantly in performance and efficiency. VP9, the successor to VP8, offers improved compression efficiency, reducing file sizes and bandwidth requirements while maintaining similar video quality. It supports higher resolutions, including 4K, and uses more advanced encoding techniques, such as better prediction modes and adaptive filtering. VP8, while still effective, lacks the advanced features of VP9 and is less efficient in handling high-resolution video. Overall, VP9 provides a more modern and efficient solution for video compression compared to VP8.
VP9 vs H.264
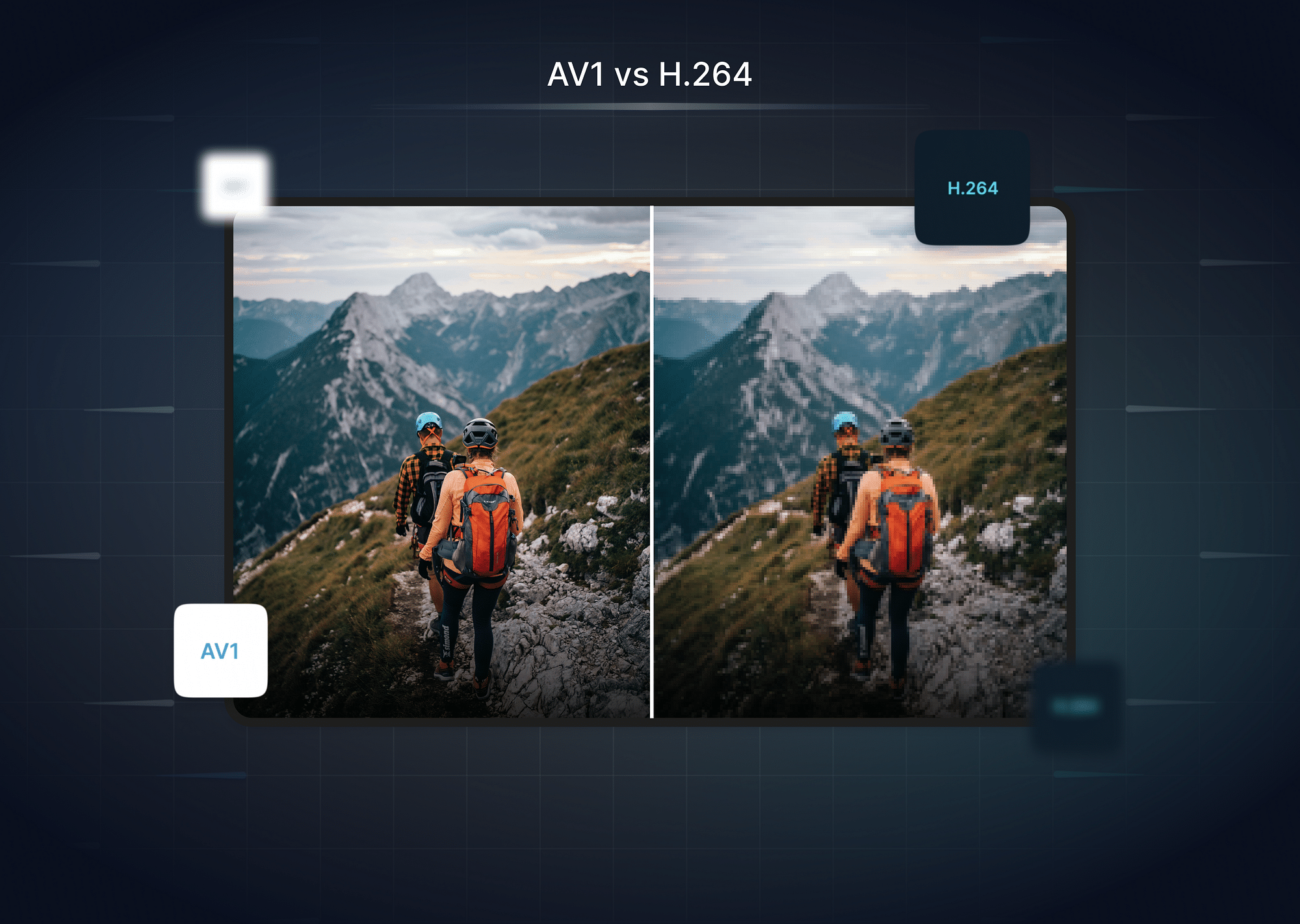
The H.264 codec compresses large amounts of information from video files to enable them to be streamed online. The HD images that H.264 works with are 1280x720 pixels, which is 720p resolution, or 1920x1080 pixels, which is 1080p resolution. With 4K , on the other hand, the total number of pixels are 3840x2160. Such a drastic increase in the level of detailing demands a superior way to perform better compression in order to transmit, store, and use the data. In that context, VP9 is twice as effective as H.264, and uses only half the data to stream 4K content without compromising on quality.
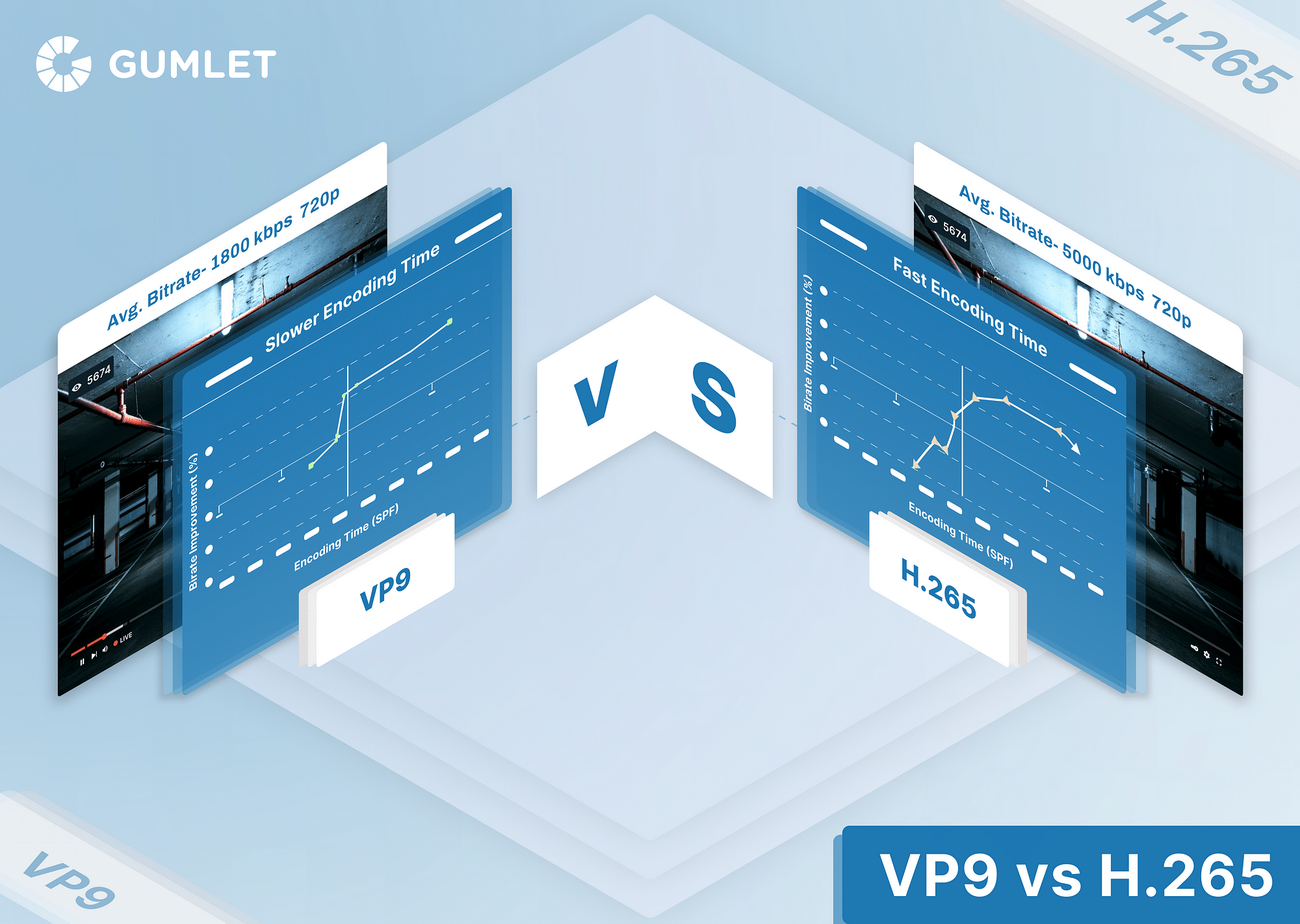
VP9 vs H.265
When talking about VP9 vs H.265, it is important to note that there are many technical similarities between the two. Even the primary goal of both these codecs is the same - to compress video files into half the bitrate to stream HD video and provide better compression techniques for 4K video to become more approachable for people with regular internet bandwidths. That said, the biggest difference between these two is that VP9 is an open-source codec and can be used by anyone, whereas H.265 requires a license to be purchased before using. In terms of usage and efficiency, these two codecs are by and large comparable.
AV1 vs VP9
The primary difference between AV1 and VP9 is that while AV1 is worthwhile only for videos with views in the mid-to-high millions, VP9 is worth considering for even videos with view counts in excess of a few thousand. Further, since VP9 is free and enjoys widespread use, it is going to be a much more viable choice in the near future.
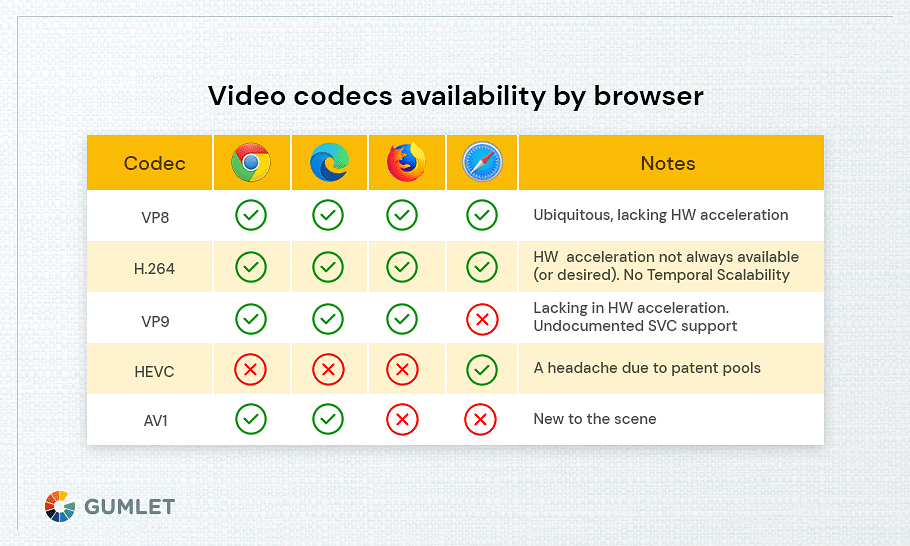
What is the Future of VP9 Codec?
The future of the VP9 codec looks promising as it continues to be a widely used standard for high-quality video streaming, particularly in 4K resolution. Its efficiency and support for advanced features, like adaptive bitrate and HDR, ensure it remains relevant. However, as newer codecs like AV1 gain traction with even better compression and performance, VP9 may gradually see reduced adoption. Despite this, VP9 will likely continue to be supported and used in various applications for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the VP9 codec has proved to be extremely useful for streaming 4K videos seamlessly, even with limited bandwidth. Being open-source, VP9 allows anyone to get started with it and compress their 4K videos in a manner like never before!
FAQs
- How to encode VP9 using FFMpeg?
Use FFmpeg with the -c:v libvpx-vp9 option and appropriate parameters for bitrate, quality, etc. Refer to FFmpeg documentation for detailed instructions.
2. How to get VP9 codec on YouTube?
YouTube automatically uses VP9 for supported videos and compatible browsers, so you don’t need to manually get the codec.
- Do video streaming services support VP9?
Yes, many streaming services, including YouTube and Netflix, support VP9 for streaming high-quality video.
- How can I troubleshoot VP9 playback issues?
Check for browser or player updates, ensure your hardware supports VP9, and clear the cache or try a different device.
- Why is YouTube video quality bad after uploading even on VP9?
YouTube processes and compresses uploaded videos, which can initially reduce quality; higher resolutions and bitrates improve final output quality.